Climate change features along the Brahmaputra Valley in the past 26 years and possible causes
Updatetime:2011-05-19From:
【Enlarge】【Reduce】
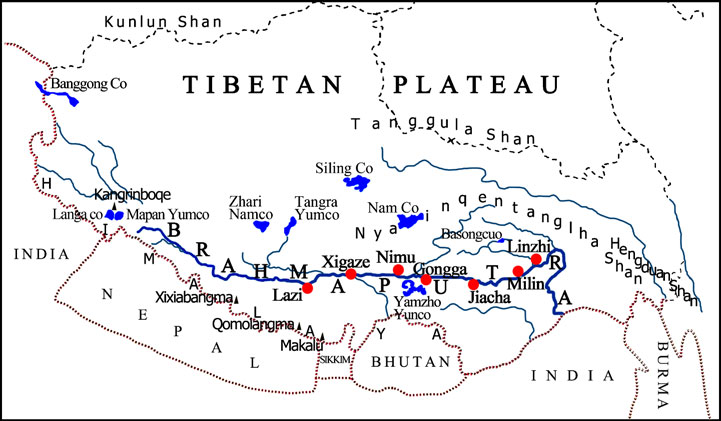
Sketch map of the Brahmaputra Valley and seven observational stations. The thick solid line means the Brahmaputra River and seven solid dots mean seven observational stations.(image by Climatic Change)
Through analyzing the changes of averaged temperature and precipitation along the Brahmaputra Valley from 1980 to 2005 and investigating the correlation between atmospheric circulation indices and these changes, the respondence of the Brahmaputra Valley to the global warming had been analyzed in the research. It is found that the Brahmaputra Valley climate became warmer and wetter from 1980 to 2005, and the change magnitude is higher than that over the whole Tibetan Plateau. Therefore, the respondence of the Brahmaputra Valley to the global warming is more evident than that of the whole plateau during the period. The relationship between atmospheric circulation indices and the regional climate change is significant. When North Atlantic Oscillation index is higher in summer, the climate of the Brahmaputra Valley becomes warmer and dryer; vice versa. When South Oscillation index is higher, it becomes warmer and wetter; vice versa.Worthy of note,the results in this research only emphasize some evidence of change in temperature and precipitation over the Brahmaputra Valley during 1980–2005.
The research was subsidized by the Chinese National Key Programme for Developing Basic Sciences (2010CB951701), National Natural Science Foundation of China(40825015, 40810059006 and 41075053), EU Sixth Framework Programme BRAHMATWINN(FP6-036952) and EU Seventh Framework Programme CEOP-AEGIS (212912).
Full text Download:http://www.springerlink.com/content/k77h04685602042t/
Appendix




