Researchers Realize Persistently Photocatalytic Uranium Extraction Using Light-storage Catalyst
Updatetime:2023-03-17From:
【Enlarge】【Reduce】
The photocatalytic reduction of soluble U(VI) showed broad prospect for the separation and extraction of uranium from solutions.
However, the photocatalytic reactions strongly depended on light irradiation, and the reduced U(IV) products could be re-oxidized when light irradiation ceases, leading to the redissolution of extracted uranium.
Recently, researchers from the Northwest Institute of Eco-Environment and Resources, CAS, now report a K+-doped and cyanamide-functionalized PHI (K-CN-PHI) for the persistent photocatalytic reduction of U(VI).
The study was published in Advanced Science on Dec. 13, 2022.
The result indicated that K-CN-PHI showed a high photocatalytic reactivity for the reduction of U(VI), being 47 times greater than pristine carbon nitride.
Interestingly, K-CN-PHI could be "charged" to form long-lived (more than 3 days) free radicals under photo-excitation. By the charged K-CN-PHI, all U(VI) could be reduced within 1 min in the dark.
This study provides a novel solution for the separation and extraction of uranium in both light and dark conditions, broadening the practical applications of the photocatalytic extraction of U(VI).
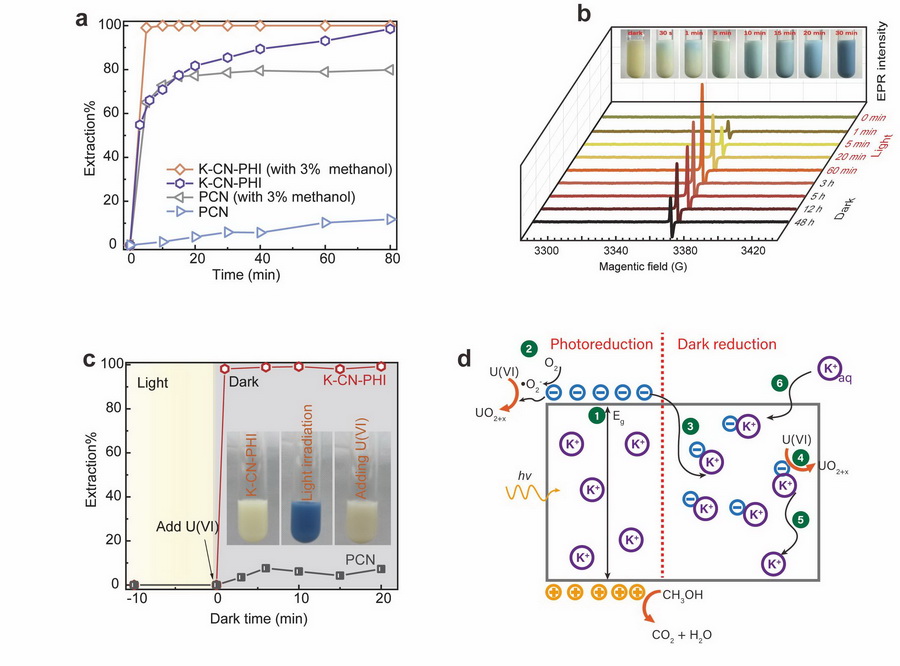
(a) Photocatalytic kinetics of U(VI) on PCN and K-CN-PHI. (b) EPR signals of the K-CN-PHI suspension collected under different irradiation times and dark times. (c) Dark reaction kinetics of U(VI) over PCN and K-CN-PHI obtained by spiking U(VI) into pre-irradiated suspensions (pre-irradiation time = 10 min). (d) Schematic diagram of the mechanisms for the photo- and dark reduction of U(VI) on K-CN-PHI. (Image by FAN Qiaohui)
Contact:
FAN Qiaohui
E-mail: fanqh@lzb.ac.cn
Appendix




