Biocrusts Reveal Ability to Form Self-Organized Patterns and Potentially Influence Dryland Ecosystem Functioning
Updatetime:2025-07-30From:西北生态环境资源研究院
【Enlarge】【Reduce】
Biocrusts, which consist of organisms such as lichens and mosses, play a vital role in dryland ecosystems. Their spatial distribution, which often exhibits Turing patterns, is fundamental to the functioning of these ecosystems. However, the mechanisms underlying the formation of these patterns and their ecological significance remain unclear.
Researchers discovered that the dynamics of biocrusts in drylands are regulated by spatial and temporal scale-dependent feedbacks, ultimately leading to the formation of self-organized Turing patterns. This self-organizing ability of biocrusts has significant implications for ecosystem functions and the resilience of dryland ecosystems.
A further finding is field measurements of biocrust performance at the center and edge of patches of varying sizes across succession stages further verify the asynchronous nature of scale-dependent feedbacks.
According to the authors, understanding the self-organization processes within biocrust communities can provide valuable insights into the connections between spatial patterns and ecosystem functionality. This knowledge may also help predict how biocrusts and dryland ecosystems will respond to environmental changes.
This work was published in PNAS on July 21, 2025.
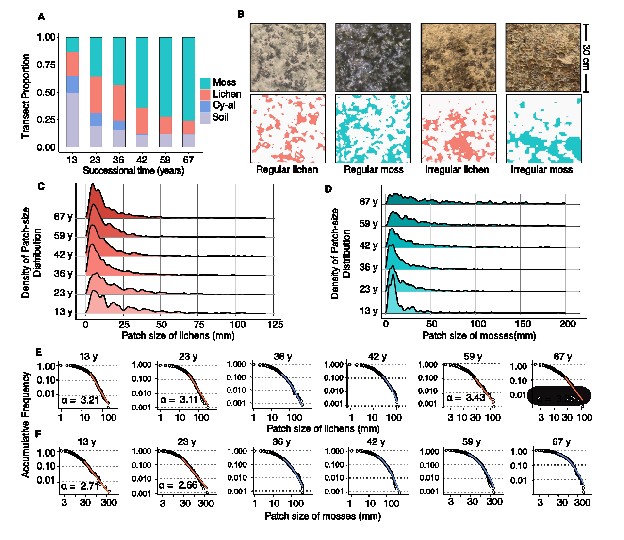
Change of composition and patch size distribution of biocrusts along successional gradient (Image from NIEER)
Appendix




