Features and Degradation of Frozen Ground in the Sources Area
Updatetime:2010-07-17From:
【Enlarge】【Reduce】
The Sources Area of the Yellow River (SAYR) is located in the transitional, mosaicked zones of seasonally frozen ground, and isolated patched permafrost, discontinuous and continuous permafrost on the northeastern Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Vertically, permafrost can be attached or detached from seasonal frost action, and the latter can be further divided into three types: shallowly-buried (≤8 m), deeply-buried (>8 m), and double-layered permafrost.
Since the 1980s, air temperatures in the SAYR have been rising at an average rate of 0.02 ℃·a-1 and human economic activities have been ever increasing, resulting in a regional degradation of permafrost. The lower limit of permafrost has elevated by 50~80 m. The average maximum depth of frost penetration has declined by 12 cm in the areas of seasonally frozen ground. The temperatures of suprapermafrost water have increased by 0.5~0.7 ℃.
The general trends of permafrost degradation include reduction in areal extent (from continuous or discontinuous permafrost to isolated patches of permafrost) and thickness, and expansion of taliks. Some permafrost patches have been converted to seasonally frozen ground.
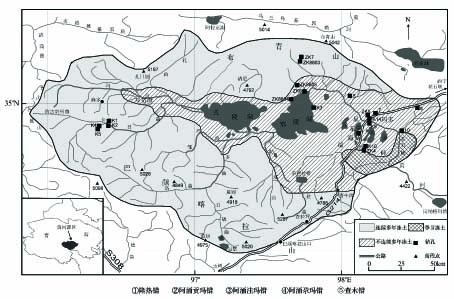
together with the locations of the boreholes
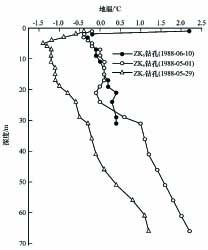
ZK5, ZK6 and ZK6
Appendix




