Mechanism of Photosynthetic Recovery of Biological Soil Crusts after the Removal of Sand Burial Disturbance
Updatetime:2010-12-03From:
【Enlarge】【Reduce】
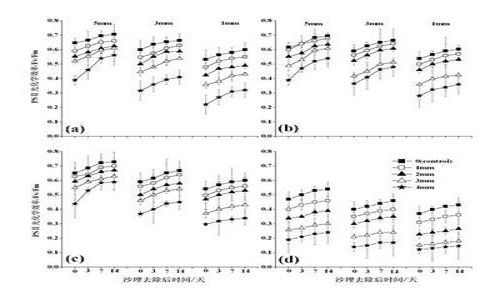
Based on continuous measurements of photosynthesis, dark respiration and chlorophyll fluorescence after the removal of sand burial disturbance, we studied the mechanism of photosynthetic recovery of four typical biological soil crusts in an artificially revegetated area in the southeastern fringe of the Tengger Desert. The results exhibited a continuous increase in net photosynthetic rates and an initial decrease and later increase of dark respiratory rates of each of the four types of crusts with time lapsing after the removal of sand burial disturbance. A significant positive effect of water supply and a negative effect of burial depth on net photosynthetic rates and dark respiratory rates were found on the four types of crusts after the removal of sand burial disturbance, respectively. In addition, the progressive accretion of PSII photochemical efficiencies proved the positive mechanism of photosynthetic recovery of four typical biological soil crusts after the removal of sand burial disturbance.
issued by <<Journal of Desert Research>>
 |
Appendix




