Contrastive Study on Radiation Budget in Cropland,Grassland and Desert in Arid Area of Northwest China
Updatetime:2010-12-16From:
【Enlarge】【Reduce】
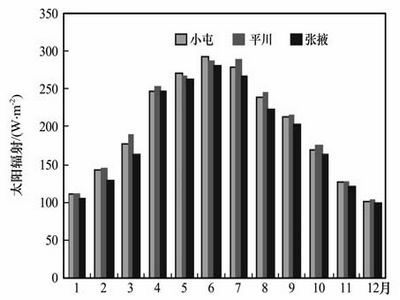
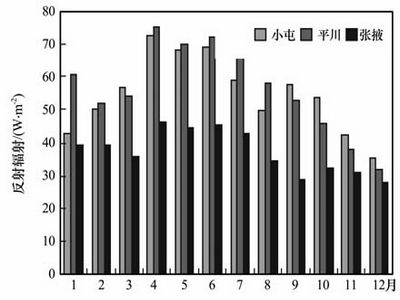
Based mainly on the experiments conducting in an intercropping field, grassland and desert in the middle reach of Heihe River basin from 1 September 2003 to 31 August 2004, the contrastive characteristics and variations of radiation budget in differentecosystems were analyzed. The results showed that the annual global solar radiation at desert and grassland stations are 6238.7 MJ·m-2 and6135.8 MJ·m-2, respectively. In intercropping field, this value is5889.0 MJ·m-2, 4% lower than that in desert station. With the increase of vegetation degree, reflected radiationdecreases in farmland and grassland which leads to albedo in weakning those areas. There is no obvious difference of downward longwave radiation in the three areas, value is a diurnal mean 280 W·m-2. On the contrary, upward longwave radiation and surface effective radiation show a significant difference in different seasons and ecosystems. As a whole, the values of upward longwave radiation and surface effective radiationin farmland and grassland are much lower of those in desert especially in the main growing seasons for the crops and pasture. The net radiation in desert, grassland and cropland are 1705.8, 2150.7 and 2458.2 MJ·m-2, respectively. The differenceof surface effective radiationresults in the significant difference of net radiation in different ecosystems.
|
Monthly of solar radiation at three stations (Picture/Plateau Meteorology) |
Monthly of reflective radiation at three stations (Picture/Plateau Meteorology) |
Appendix