Experimental Study of Effects of Artificial Dew on Bassia dasyphylla and Agriophyllum squarrosum
Updatetime:2010-12-16From:
【Enlarge】【Reduce】
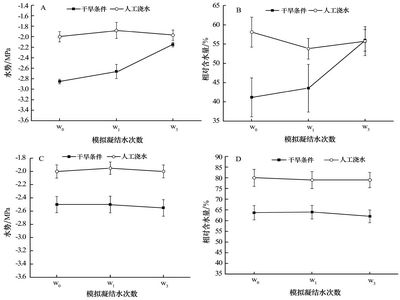
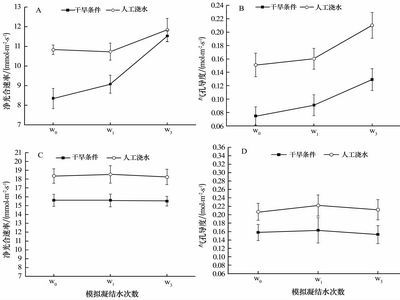
The effects of foliar absorption of dew by hairy leaves of Bassia dasyphylla and nonhairy leaves of Agriophyllum squarrosum on shoot water potential, relative water content, net photosynthesis, stomatal conductance, basal diameter, aboveground dry mass and root dry mass were investigated. Bassia dasyphylla and Agriophyllum squarrosum seedlings were subjected to contrasting water regimes (normal condition and deficient water) and three kinds of artificial dew simulation (none, once per week and three times per week). The results are as follows. Artificial dew significantly increased shoot stomatal conductance and aboveground dry mass of Bassia dasyphylla seedlings subjected to water deficient and normal condition. Obvious responses in shoot water potential, relative water content, net photosynthesis, and root dry mass were observed for Bassia dasyphylla seedlings subjected to water deficient. The little effects of dew on basal diameter were observed. No obvious effects were found in shoot water potential, net photosynthesis, stomatal conductance, basal diameter, aboveground dry mass and root dry mass of nonhairy leaves of Agriophyllum squarrosum seedlings subjected to water deficient and normal condition. Obviously, we can draw a conclusion that hairy leafs of Bassia dasyphylla may improve leaf water status by dew absorption, while nonhairy leaves of Agriophyllum squarrosum can not absorb dew.
|
Effects of artificial dew on shoot water potential and relative water content (Picture/Journal of Desert Research) |
Effects of artificial dew on net photosynthetic rate and stomatal conductance (Picture/Journal of Desert Research) |
Appendix