The Surface Energy Balance on the Qiyi Glacier in Qilian Mountains during the Ablation Period
Updatetime:2010-12-16From:
【Enlarge】【Reduce】
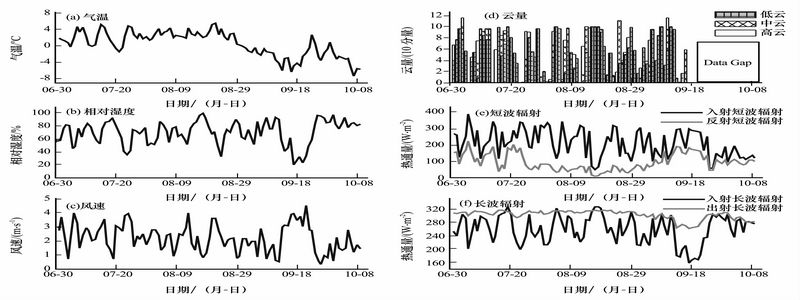
Employing the Automatic Weather Station (AWS) installed on the Qiyi Glacier in the period of 1 July to 10 October, 2007, the energy balance components including net radiation, sensible and latent heat fluxes, subsurface energy flux and the heat flux supplied by warm rainfall have been obtained and analyzed in detail. The microclimate features in summer have also been analyzed. It is revealed that the net radiation dominates the energy exchanges at the glacier-atmosphere interface; the turbulent sensible heat flux is the second remarkable energy flux. During the ablation season, the heat is consumed mainly by melting. At the end of the ablation season, the proportion of turbulent latent heat flux begins to increase. The snow/ice conductive heat flux can be neglected.
|
The daily mean air temperature(a)、relative humidity(b)、wind speed(c)、radiation(e,f) at 1.5 m height of AWS and daily mean cloud cover (Picture/Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology) |
Appendix