Remote Sensing Retrieval of Daily Evapotranspiration over the Heihe River Basin
Updatetime:2010-12-24From:
【Enlarge】【Reduce】
The estimation of evapotranspiration(ET)over heterogeneous land surface of arid and semi\|arid regions is quite complicated and significant. NOAA/AVHRRremote sensing, NCEP reanalysis grid and meteorological station data are used to estimate daily ETover the Heihe River basin based on the integrating surface energy algorithm for land model and the Penman method. As for clear days, Remote sensingmodel is used to retrieval the instantaneous ET to daily ET. FAO-17 Penman method is also used to estimate the same day′s reference crop ETby NCEP reanalysis grid data and the meteorological station data. The relationship between actual ETand the reference crop ETcan be used to calculate the actual ETbased on the results from FAO-17 Penman methodon the cloudy days. These results are validated by the observation data and other study in Heihe River basin. Integrate the remote sensing data and grid data can enhances the resolution of the NCEP grid data from 0.25 degree to 1.1 km by remote sensing data, and also make up deficiency of the remote sensing data on the cloudy days. This work will provide reference for similar research in this region.
|
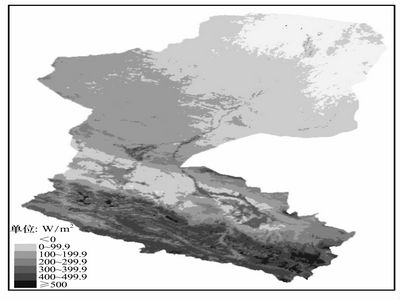
Latent heat flux distribution in Heihe (Picture/Plateau Meteorology) |
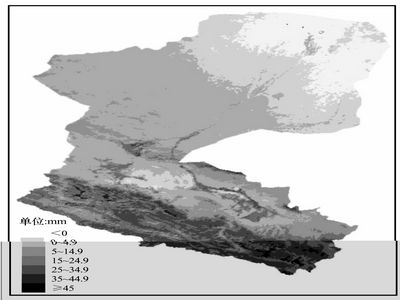
ET distribution in Heihe River basin (Picture/Plateau Meteorology) |
Appendix