Glacier Runoff Change in the Upper Stream of Yarkant River and Its Impact on River Runoff
Updatetime:2011-01-04From:
【Enlarge】【Reduce】
Yarkant River is one of the main sources of the Tarim River, which is located in the north slopes of the Karakorum Mountains. The glacier runoff is the main supply of the river runoff in Yarkant River. Based on the monthly precipitation and air temperature from the Kulukelangan Hydrological Station, a national meteorological station in the Yarkant River basin, 90-m resolution DEM and the digital vector map of glaciers during the 1970s, the glacier mass balance and glacier runoff sequence were reconstructed by a degree-day glacier melting model, and compared with short-term observations and other available results. The characteristics and trends of glacier runoff variation were analyzed. It is found that the mean annual glacier mass balance during 1961-2006 was -163.1mm per year and the total 46-year glacier mass loss was -7.5 m in thickness. There was a clearly increasing trend in glacier runoff, which is caused by net ice mass loss for the period 1961-2006. A remarkable shift from minor negative mass balance to strong negative phase has taken place since 1991, with the mean annual mass balance of -301.2 mm. The equilibrium line altitude rose up about 64.2 m during 1991-2006 as compared with the mean value over the period 1961-1990. The climate pattern has changed from warm-dry to warm-wet around 1986. The average of glacier melting depth of the upper reaches of Yarkant River was 807.7 mm during 1961-2006. Glacier melting has increased more significantly since 1990. The tight relationship between glacier runoff and mass balance indicates that glacier runoff change is mainly controlled by mass balance. The contribution of glacier runoff to river runoff in Yarkant River was approximately 51.3% during 1961-2006 and increases to approximately 63.3% after 2000. The contribution of glacier runoff to river runoff has increased significantly since 2000.
|
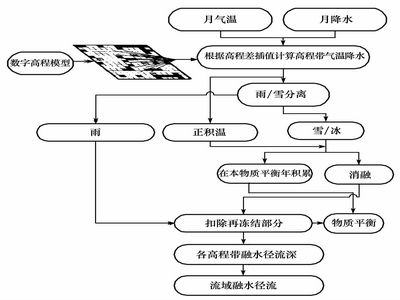
The flowchart of the degree-day glacier runoff model computing (Picture/Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology) |
Appendix