The Characteristics of Surface Albedo in Permafrost Regions of Northern Tibetan Plateau
Updatetime:2011-01-06From:
【Enlarge】【Reduce】
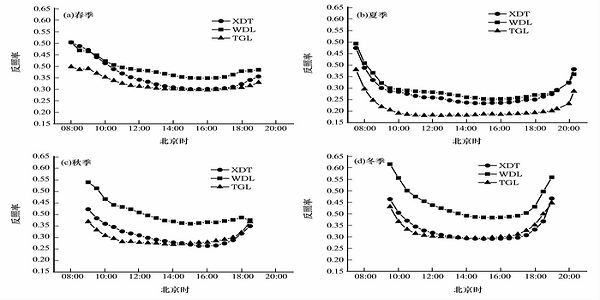
Based on the observed radiation data at automatic weather stations including Xidatan (XDT), Tanggula (TGL) and Wudaoliang (WDL) (operated by Cryosphere Research Station on Qinghai-Xizang Plateau, CAS) in 2006 and 2007, characteristics of surface albedo under different surface conditions in permafrost regions of Northern Tibetan Plateau are analyzed. The results indicated that surface albedo in these regions shows obvious diurnal variation characteristics in the four seasons. The diurnal variation curves present "U" shapes. The values of surface albedo are larger at sunrise and sunset and smaller at noon. The daily and monthly mean values of surface albedo have similar annual variation characteristics. The values of surface albedo are much larger in winter half-year than summer half-year. By the impact of snow cover, the annual average of surface albedo in these regions is larger than other regions of the plateau. The values decrease in the following order: winter, spring, autumn and summer. Under different surface conditions, the values of surface albedo rank as alpine meadow (TGL)<alpine grassland (XDT)<desert steppe(WDL).
|
The diurnal variations of the surface albedo in Xidatan (XDT), Wudaoliang (WDL)and Tanggula (TGL) (Picture/Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology) |
Appendix