Desertification Process and Its Spatial Differentiation in Arid Areas of Northwest China
Updatetime:2011-01-20From:
【Enlarge】【Reduce】
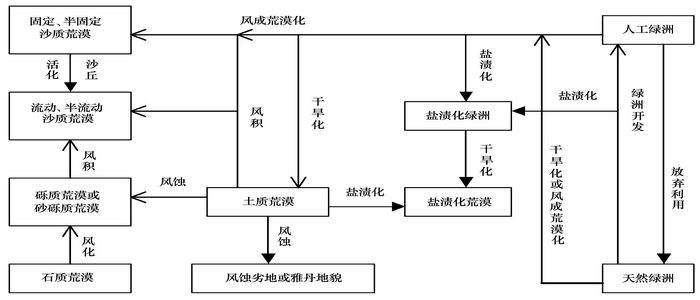
Land desertification in arid areas of northwest China could be classified as two types: desert desertification and oasis desertification. Desert desertification presents mostly aeolian desertification, which occurs mainly in terrene desert and sandy desert. As final result of desertification, terrene desert turns into sandy desert, gravel desert or aeolian land. Desertification of sandy desert is a process that fixed and semi\|fixed desert turn into mobile or semi\|mobile desert, which results finally in formation of mobile desert. Oasis desertification includes main three types: aridilization, aeolian desertification and salinization. Oasis aridilization results normally in degeneration and death of oasis vegetation, which causes oasis lessening. Aridilization is commonly piled by aeolian desertification in marginal part of oasis, which results in an incursion of mobile sand to oasis. If water source is cut entirely, oasis will disappear and become finally sandy desert or aeolian land. Oasis salinization results from excess irrigation in farmland, which causes hoist of ground water level and congregation of salt in surface soil layer from underlying layer, resulting finally in formation of salt oasis or salt desert. In northwest China, desertification of terrene desert exists mostly in east part of Alax area, Inner Mongolia, alluvium fan in south piedmont of Tianshan Mountains, desert steppe area of north Junggar Basin. Desertification of sand desert occurs mainly in Gurbantunggut Desert of Junggar Basin. Oasis aridilization and aeolian desertification are typical in Minqin Oasis of Gansu, and oasis salinization distributes mainly in Akesu oasis and Kashi oasis of Xinjiang.
|
Transform among different landscapes in desertification process (Picture/Journal of Desert Research) |
Appendix