The Ecohydrology of the Soil Vegetation System Restoration in Arid Zones: A Review
Updatetime:2011-02-05From:
【Enlarge】【Reduce】
Arid zones , which cover approximately 40 percent of the earth´s land surface , support complicated and widely varied ecological systems . As such , arid zones are an important composition of the global ter restrial ecosystem , and water is the key and abiotic limited factor in ecosystem-driven processes in these areas.Ecohydrology is a new cross discipline that provides , in an objective and comp rehensive manner , novel ideas and approaches to the evaluation of the interaction and feedback mechanisms involved in the soil vegetation systems in arid zones . In addition , ecohydrology provides a theoretical basis of ecological restoration that is centered on vegetation construction. In the research, long-term monitoring and local observations in the transitional belt between a desertified steppe and a steppified desert at the Shapotou Desert Research and Experiment Station , Tengger Desert , in northern China , were evaluated. The primary achievements and related research progress regarding ecohydrology in arid zones were analyzed and summarized , as a keystone , and the response of soil ecohydrological processes to the changes in the species composition , structure , and function of sandland vegetation was discussed. Meanwhile , the long-term ecological effects and mechanism of regulation of vegetation on soil habitat and on water-cycling were considered. As a vital participant in the ecohydrological p rocesses of soil vegetation systems , the studies on biological soil crusts was also summarized , and related theoretical models of restoration based on the water balance was reviewed.
|
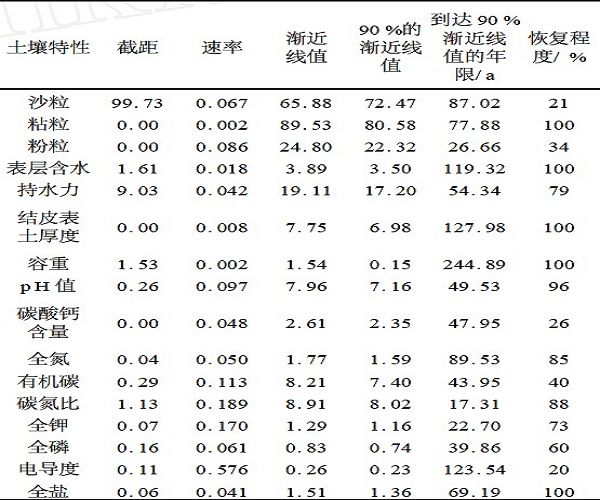
Intercepts、rate parameters and asymptote values of curves f itted to the recovery of soil physical、chemical characteristics of a chronosequence (Picture/Journal of Desert Research) |
Appendix