Observational Study of the Surface Energy Closure in the Semi-Arid Regions of Loess Plateau in Late Spring
Updatetime:2011-02-08From:
【Enlarge】【Reduce】
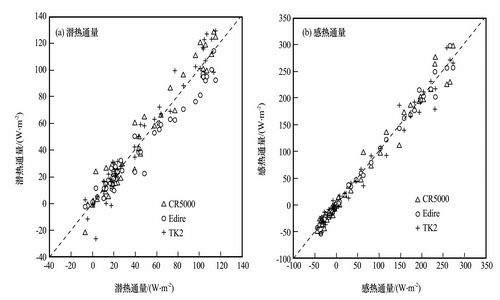
The characteristics of surface layer’s turbulent flux ,surface energy balance and energy closure in the semi-arid regions of Loess Plateau are analyzed , using the data observed from the Semi-Arid Climate and Environment Observatory of Lanzhou University. The observatory is about 48 km away from t he center of Lanzhou city , situated at the southern bank of the Yellow River in Gansu province (35.57°N , 104.08°E) . It is situated on the China-Loess Plateau , about 1 965. 8 m above sea level . The topography around the observatory is characterized by the Loess Plateau consisting of plain , ridge and mound , etc , with the elevation ranging between 1 714 -2 089 m. There is loess soil in the terrace , ridge and mound. The terrain where the measurements are carried out is flat and covered with short glass. The annual mean temperature is 6.7 ℃, the January mean temperature is - 8 ℃and the July mean temperature is 19 ℃.The annual mean precipitation is 381.8 mm , and the relative humidity is 63 %. In this research , using the 11-day observation from May 21 —31 , 2006 ,the data quality and the characteristics of surface layerps turbulent fluxes , surface energy balance and energy closure in the semi-arid region of Loess Plateau are analyzed. The results display that : the average period of 30 min~1 h is the best time scale in the observatory. The output of turbulent fluxes is the best by using the soft of EdiRe , as compared with using the soft TK2 and CR5000 automatic data recorder . Obviously , there is a correlation between the turbulent flux of surface layer and the surface moisture condition. In the dry period , the surface sensible heat flux is dominant , showing the characteristics of arid region ; in the wet period ,sensible heat flux is equal to latent heat flux , similar to the humid areas. The surface energy balance closure rate in the observatory is as high as 85 %,which is better level as compared with other observations.
|
Latent heat fluxes (a) and sensible heat fluxes (b) calculated from different output manners (Picture/Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology) |
Appendix