Experimental Study of Convective Characteristicsof Block-Stone Embankment
Updatetime:2013-01-07From:
【Enlarge】【Reduce】
Active cooling embankment made of block-stone in permafrost regions is an important engineering measure, which has been widely used in national key projects, such as Qinghai-Tibet Railway. So it is great significant to study air flow characteristics for its structural optimization and performance improvement, and air flow characteristics in block-stone due to temperature difference and micro wind speed are always the problems that need to be solved. In this study, air flow characteristics in block-stone are got at the first time by high-precision macro wind-speed detector. It is found that the cooling process is closely related to the process of natural convection in block-stone in the condition of boundary temperature fluctuating and rapidly completing in the convective process; warming-up process is largely aroused by the heat conduction, which results in asymmetry of the temperature curve, and becomes obvious with depth increasing; however, the convective process exists only in the processes of fast cooling stage and cooling stagnation stage; temperature difference in block-stone is the key control factor of the convection and its intensity; when temperature difference reaches a certain value, convective velocity increases with temperature difference, meanwhile the change of air temperature also have an impact on the air flow process. Air flow process in block-stone is a transfer process. The experimental results have a great significance for further understanding the cooling mechanism, improving this measure and selecting the relevant simulation parameters, effectively applying to high-grade highway construction in permafrost regions as well.
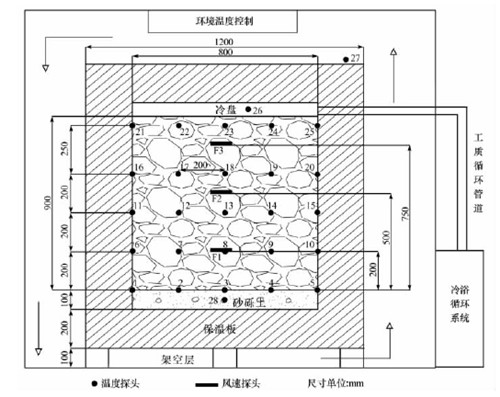
The experiment model and observation system
Appendix





