Response of Photosynthetic Characteristics of C3 Desert Plant Reaumuria soongorica and C4 Desert Plant Salsola passerina to Different Drought Degrees
Updatetime:2013-01-14From:
【Enlarge】【Reduce】
The mixed community of C3 and C4 plants is easily seen in grassland ecosystem, but hardly seen in desert ecosystem. In desert regions of China, some C3 and C4 shrubs coexist in particular manners in some specific habitats and adapt to the extreme arid environment, which is associated with high temperature and intensive radiation. The mixed communities of C3 undershrub Reaumuria soongorica and C4 subshrub Salsola passerina in the Heihe River Basin in Hexi Corridor were investigated. The physiological characteristics of gas exchange of R. soongorica and S. passerina in the mixed community were determined under different drought degrees. Results showed that net photosynthetic rate (Pn), transpiration rate (E), stomatal conductance (Gs) of R. soongorica were all higher than S. passerina, while water use efficiency of S. passerina was higher than R. soongorica. The differential responses of the two species to severe habitat shows that R. soongorica and S. passerina take different strategies for survival when suffering water scarcity in the same desert habitats: R. soongorica uses the means of maintaining a higher net photosynthetic rate and a higher transpiration rate to survive, while S. passerina survives here through the higher water use efficiency.
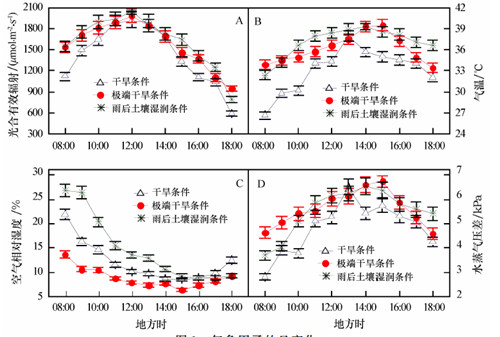
Diurnal changes of photosynthetic photon flux density(A),air temperature(B),air relative humidity(C),and vapor pressure deficit from leaf to air(D)
Appendix





