Vulnerability of an inland river basin water resource system under the background of future accelerated glacier melt: A case of Yarkent River Basin in arid Northwest China
Updatetime:2013-01-30From:
【Enlarge】【Reduce】
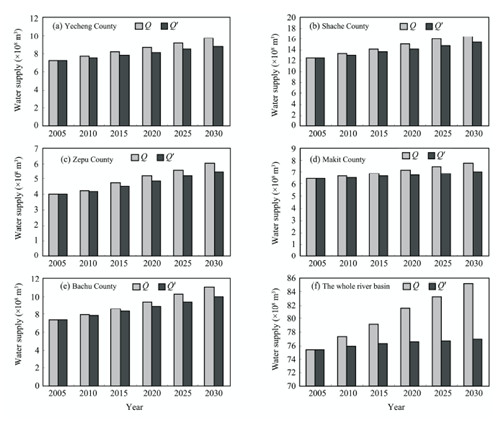
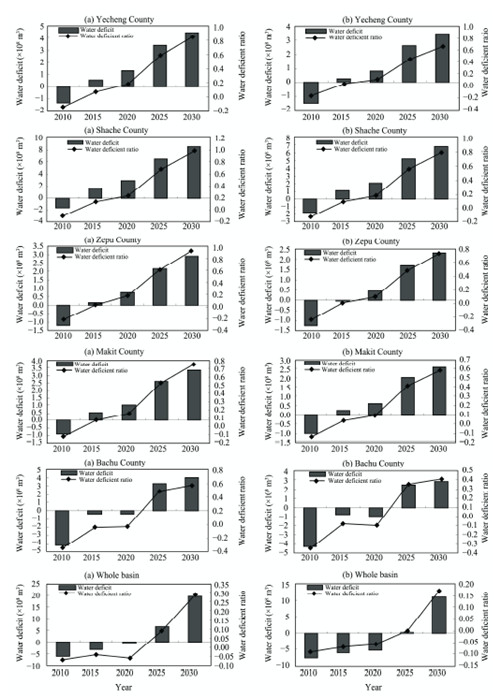
The available water resources of the Yarkent River Basin will constantly increase over the next 20 years driven by climate warming and accelerated glacier melt, and the increment of glacial melt water becomes the most important contributor to this increase. Driven mainly by the improvement of water-saving technology, future water demand of the basin will constantly decrease, but the water demand of each county will remain quite large in the next 10 years with the present low efficiency of water use. Under the combined act of natural and human factors, the water resource system of the whole basin may be quite vulnerable in the next 10 years, and then afterwards will become less vulnerable. Further analysis shows that climate warming and resulting accelerated glacier melt may relieve the strain between supply and demand of water and diminish the vulnerability of water resource system of the Yarkent River Basin through increased glacial melt water in the next 20 years.
Download
Appendix




