Numerical Simulation of Impact of Ecological Environment Change on Lake Effect in the Source Region of the Yellow River
Updatetime:2013-07-17From:
【Enlarge】【Reduce】
A three-dimensional mesoscale atmospheric model WRF is used to examine the characteristic of lake effect over Lake Ngoring in the upper reach of the Yellow River and the influence of terrestrial environment change on the lake effect. Three groups of experiments have been simulated which include environmental improvement, status quo, degradation. The main results show: (1) From noon to nightfall in sunny summer, there is a clear lake-breeze circulation in Lake Ngoring; both sensible heat flux and latent heat flux are small over the lake in daytime, moreover, there is a strong cold (warm) lake effect over Lake Ngoring region in daytime (nighttime); the specific humidity over lake is larger than that over land in surface layer, but there is converse above it; the water vapor wall and high value areas of sensible flux can be found on land along the lake under the influence of lake breezes. (2) Environment degradation results in an enhanced lake-breeze circulation and higher water vapor wall. In addition, the difference of the boundary layer height increases between land and lake; for the different surface characteristics, the changes of sensible heat and latent heat fluxes over land are much more than that over the lake. (3) Environment changes impact on the distributions of air temperature and specific humidity in the bottom and top of the boundary layer through the underlying surface and the lake breeze, respectively, as a result, there is a reverse trend in different heights.
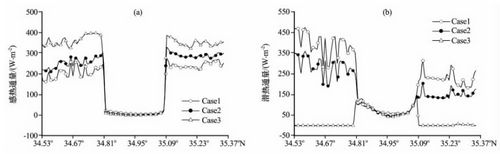
The zonal distributions of sensible heat flux(a) and latent heat flux(b) along 97.723°E in three experiments at 14:00 on 23 July 2010
Download from the attachment




