WRF Model Reproduces the Surface Heat Flux on the Underlying Surface of Qinghai-Xizang Plateau
Updatetime:2013-11-05From:
【Enlarge】【Reduce】
Qinghai-Xizang Plateau has a special location in world. The weather of Eastern China, East Asian and global climate are influenced by the heating power and plateau power. A very special boundary layer is formed by the high elevation of plateau, and its average elevation is over 4000m, the atmosphere is influenced by the thermal effects and dynamic effects. Therefore, it is important to study the boundary layer of atmosphere on plateau, especially the observation and analysis of the heat flux at the land surface.
Based on the observation data from July to August in 2007 derived from Nagqu station of Plateau Climate and Environment, CAREERI (Cold and Arid Regions Environmental and Engineering Research Institute) and WRF model, the characteristics of land surface heat flux, land surface radiation and energy flux exchange were analyzed in the northern Qinghai-Xizang Plateau. The four groups of sensitive experiments which changed soil moisture and vegetation coverage in initial model input field were designed. The simulated radiation and energy exchange is analyzed in the north Qinghai-Xizang Plateau. WRF model can reproduce the daily variation of land surface fluxes in the Qinghai-Xizang Plateau. When the initial values of soil moisture and vegetation coverage were changed to close to in-situ data, the modeling results show good outcome. Although WRF model can simulate well land surface heat fluxes in the Qinghai-Xizang Plateau, but it still exist error and shortage for land surface heat fluxes. All of these facts which land surface heat fluxes were changed clearly will provide strong evidence for the study of energy and water cycle in the Qinghai-Xizang Plateau. It is the most obvious that the simulated results of changes of sensible and latent heat fluxes, are much closed to the observation data.
This program is financially supported by Global Change Research National Major Scientific Research Projects (2010CB951701), National Natural Sciences Foundation of China (41375009, 41275010, 41275028) and Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (WK2080000036). This paper has been published on the Journal of Plateau Meteorology, Vol. 32, No.5, Oct. 2013. The full text can be seen: http://gyqx.westgis.ac.cn/EN/abstract/abstract3390.shtml
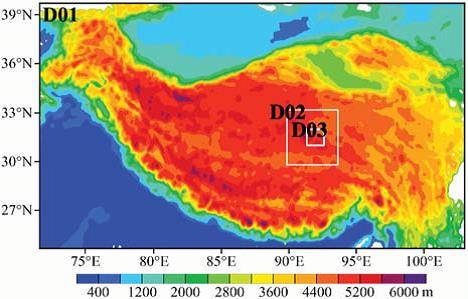
Fig. Schematic diagram of three domains in WRF model
Appendix




