Tamarix ramosissima stand evapotranspiration and its association with hydroclimatic factors in an arid region in northwest China
Updatetime:2017-04-18From:
【Enlarge】【Reduce】
There is currently only limited quantitative data available on riparian forest evapotranspiration (ET) of saltcedar (Tamarix
This was comparable to results from the lower Tarim River basin in central Asia where
Moreover, environmental parameters, such as climate and soil water content, accounted for at least 68%–78% of hourly and daily ET variation, respectively. Soil water factors were more important in accounting for daily ET variation than climate factors, but the opposite was true on a hourly timescale. Results showed that lower water use in
This research result is published on Journal of Arid Environments
Keywords: Evapotranspiration;
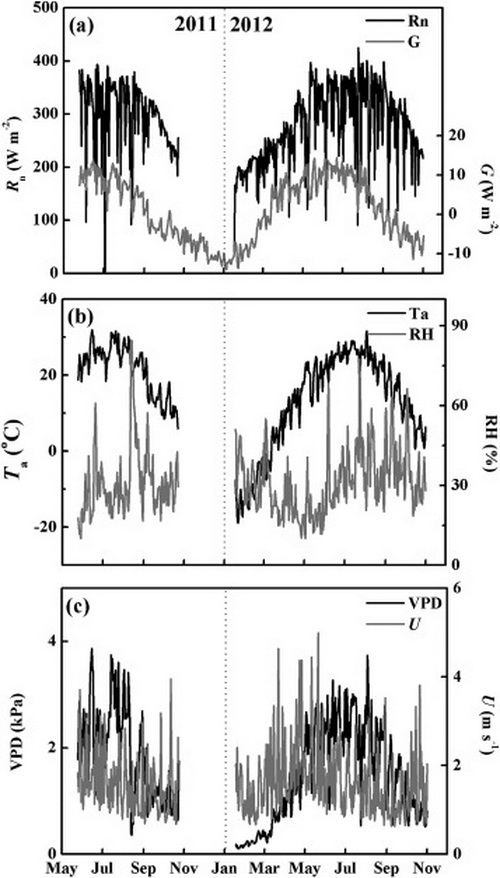
Fig. Daily variation in meteorological factors: (a) net radiation (Rn, MJ m−2 d−1) and soil heat flux (G, MJ m−2 d−1); (b) air temperature (Ta, °C) and relative humidity (RH, %); and (c) the vapor pressure deficit (VPD, kPa) and wind speed (U, m s−1) for
Appendix




