Elements and Transport Routes of Atmospheric Pollutants in Glaciers of the Northeastern Tibetan Plateau Revealed
Updatetime:2019-07-25From:
【Enlarge】【Reduce】
Atmospheric deposition and contamination of trace elements mainly come from anthropogenic emissions, which can be transported from emission sources to deposition sites around the globe and exert an adverse impact on the environment and human health.
However, large-scale investigations on the transport and deposition of trace elements across the northeastern Tibetan Plateau (TP) and its surrounding regions remain very limited owing to the lack of trace element contamination data in high-elevation snowpacks of remote regions and the inability to accurately assess impacts from human activities.
Recently, a research group from Northwest Institute of Eco-Environment and Resources (NIEER) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences measured Al and 13 trace elements in glacier snowpacks in the northeastern TP to investigate the transport and deposition of atmospheric pollutants in remote glaciers.
The results suggest that trace element deposition among the four glaciers differ significantly with higher concentrations of Co, Cr, Mo, Ni, and V at the Miaoergou Glacier, higher of As, Cd, Cs, Cu, Pb, and Sb at the Yuzhufeng, and higher of Zn at the Qiyi glaciers.
The results are compared with remote eastern Antarctica, which shows that the concentrations of trace elements in all four sites are 2-100 times higher than those in the compared region, thereby reflecting very serious atmospheric pollution in the northeastern TP.
Besides, meteorological data are also employed to identify the potential transport of pollutants to remote glaciers in the northeastern TP. In general, the results suggest two different pollutant transport routes (Central Asia and South Asia) to the northeastern TP.
This study will provides a new understanding of the large-scale transport and deposition of trace elements in the remote glacier basins of the northeastern TP.
The study entitled “Atmospheric deposition and contamination of trace elements in snowpacks of mountain glaciers in the northeastern Tibetan Plateau” was published in Science of the Total Environment.
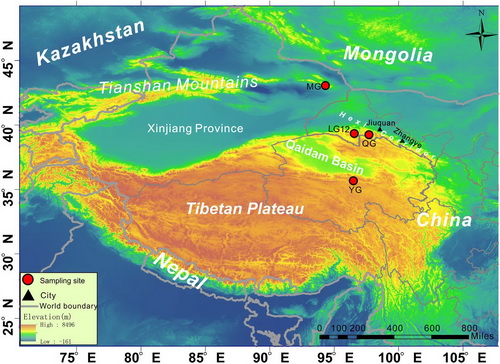
Map showing the study areas and sampling sites in the northeastern Tibetan Plateau, including the QG (Qiyi Glacier), LG12 (Laohugou Glacier No. 12), YG (Yuzhufeng Glacier), and MG (Miaoergou Glacier). (Image by KANG Shichang)
Contact:
KANG Shichang
E-mail: shichang.kang@lzb.ac.cn
State Key Laboratory of Cryosphere Sciences, Northwest Institute of Eco-Environment and Resources, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Lanzhou 730000, China.
Appendix




