-
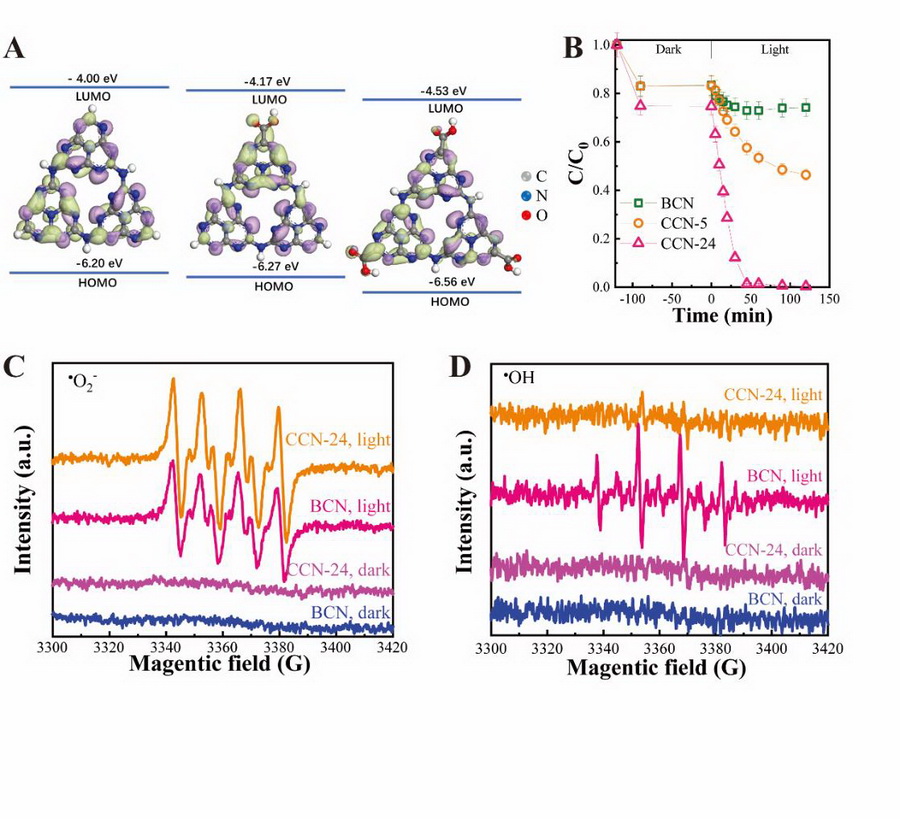
Photocatalytic U(VI) Reduction Assists to Extract Uranium from Seawater
In this study, scientists from Northwest Institute of Eco-Environment and Resources (NIEER) of Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) were devoted to realizing the photo-reduction of U(VI) in carbonates-containing system by developing a highly efficient photocatalyst.
2021-04-22 -
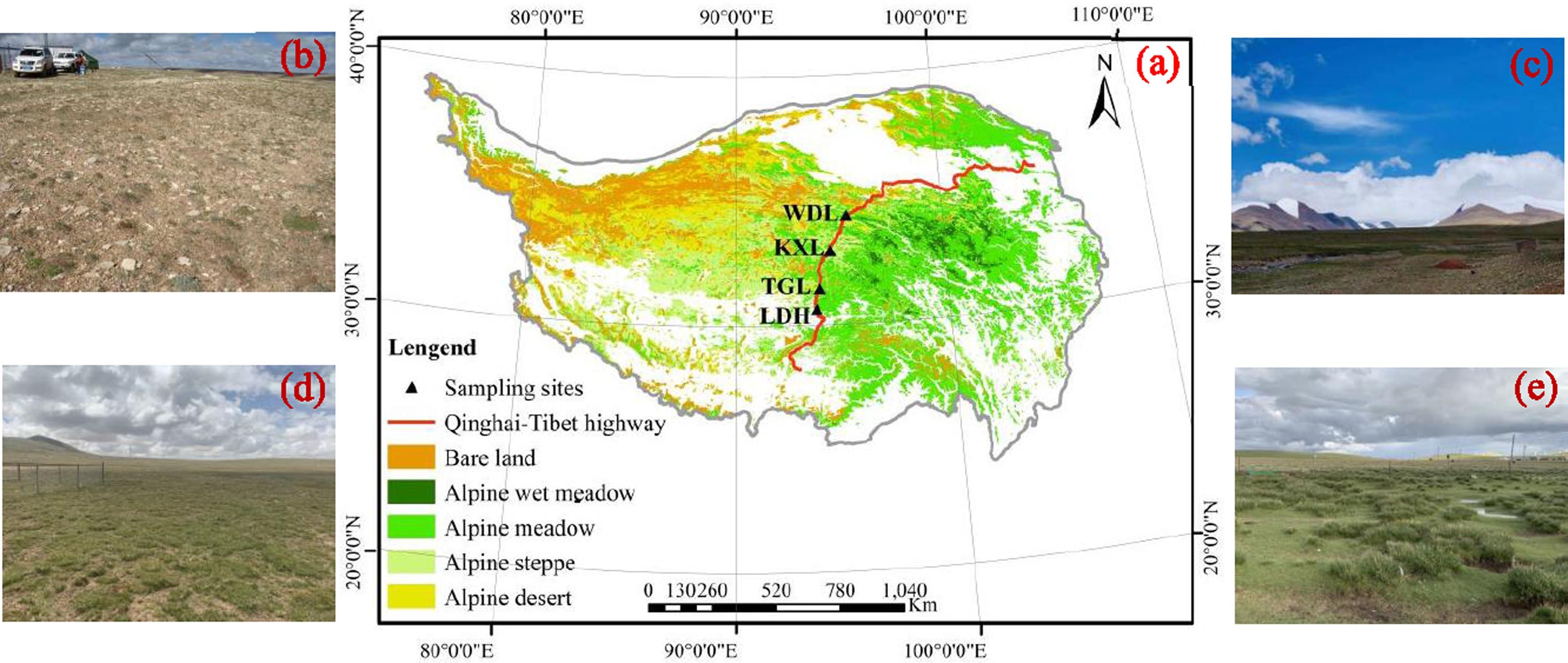
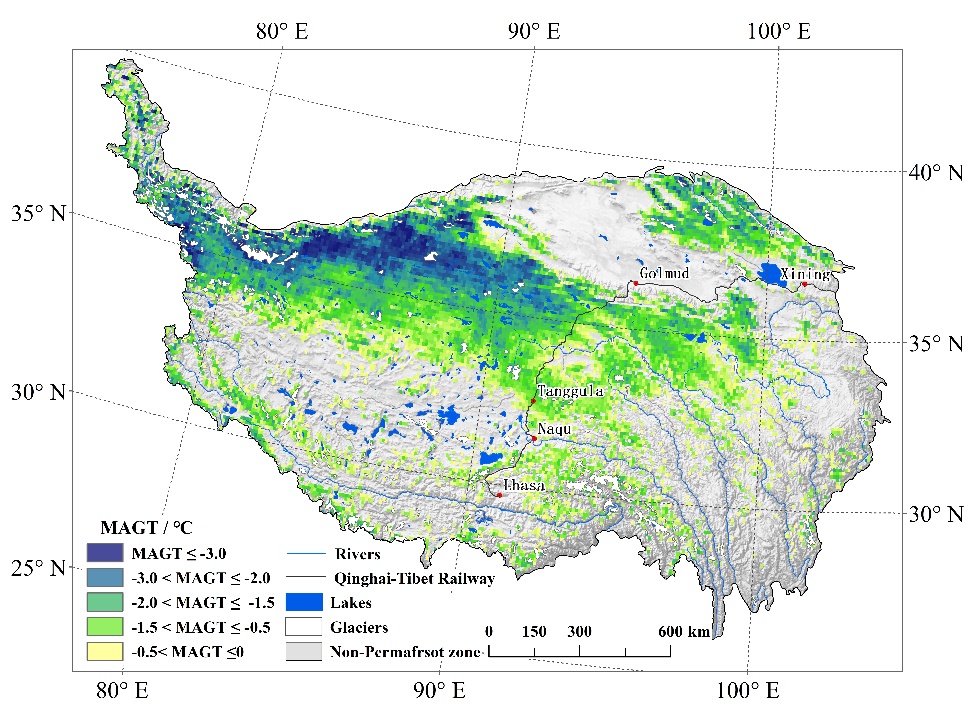
Scientists Reveal Responses of Various Permafrost Ecosystems to Climate Warming
Using the dynamic vegetation model, combined with the data of soil water, heat and carbon flux at long-term observation points, a research team led by Prof. WU Tonghua from Northwest Institute of Eco-Environment and Resources (NIEER) of Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) systematically studied the global change of ca...
2021-04-20 -
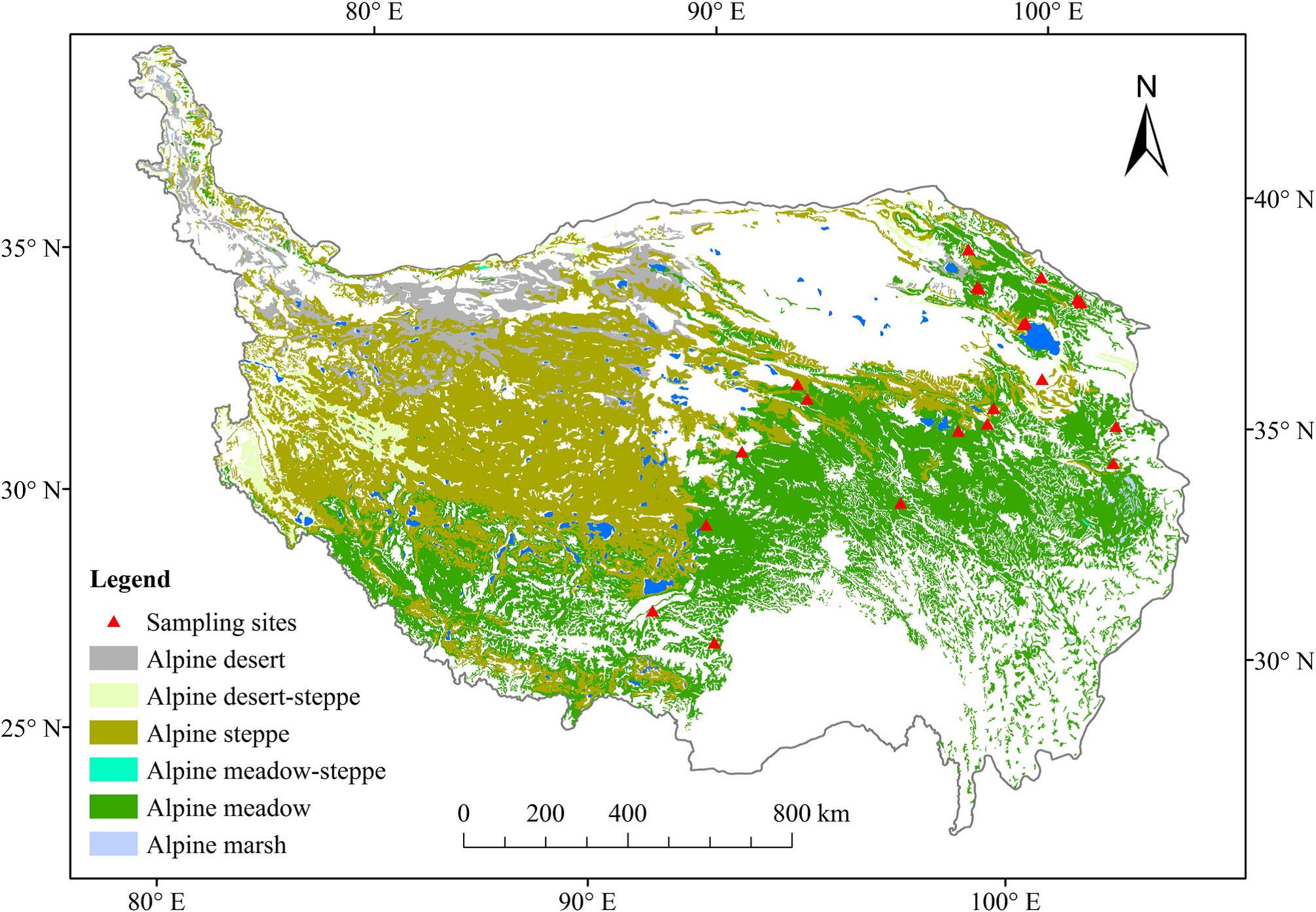
Scientists Reveal Responses of Carbon and Nitrogen cycles to Grassland Degradation
Recently, scientists from Northwest Institute of Eco-Environment and Resources (NIEER) of Chinese Academy of Sciences selected five degradation stages including intact, slight degradation, moderate degradation, severe degradation, and very severe degradation to explore the degradation effects on C and N cycles on th...
2021-04-15 -
-
-
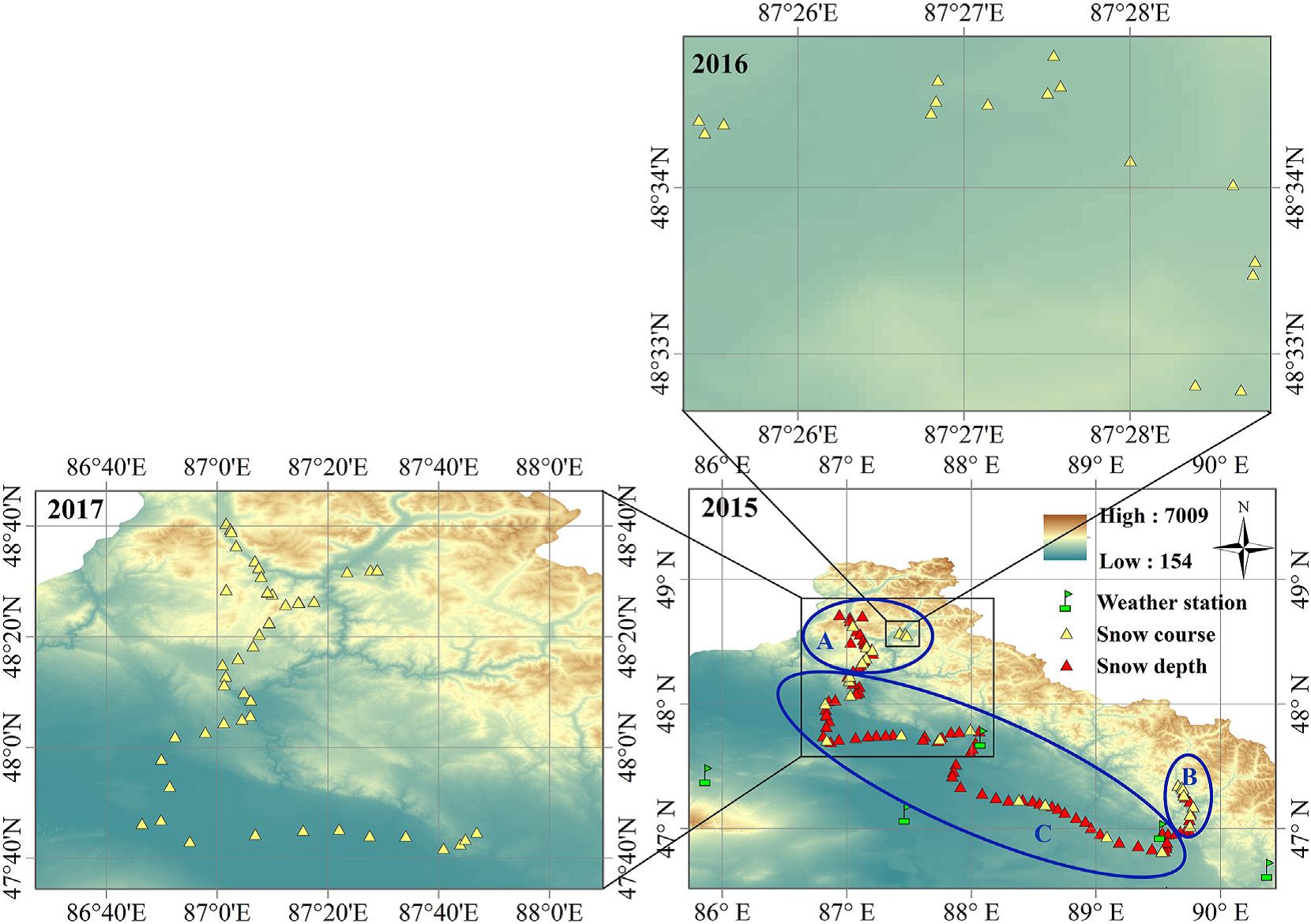
Scientists Reveal Snow Cover Distribution in Southern Altai Mountains
Recently, researchers from Northwest Institute of Eco-Environment and Resources (NIEER), Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), together with their colleagues from Lanzhou University, investigated the spatial characteristics of snow depth, snow water equivalent (SWE), and snow density in the southern Altai Mountains.
2021-04-02




