Experimental Study of the Tibetan Silty Clay under Freeze-Thaw Cycles
Updatetime:2013-07-17From:
【Enlarge】【Reduce】
The Tibetan silty clay along the Qinghai-Tibet Highway was taken as the study object. The distribution of temperature and water content and freeze-thaw displacement of the specimens after 1, 2, 3 and 4 freeze-thaw cycles were obtained and analyzed. It is found that after freeze-thaw cycles, the temperature fields of the specimens will be more stable and proportionate distribution, the 0 ℃ isotherm and subzero isotherm will be deeper. The water content profile of the specimens can be divided into four sections. The first section is the surface layer one of high water content with ice crystal accumulation. The second section is water content equilibrium one with low temperature gradient. The third section is high water content one with ice lens and ice layers. The fourth section is lower water content one at high temperature. For the first freeze-thaw cycle, there are large frost heaving displacement, even reaching dozens of millimeters, and large relative freeze-thaw displacement, even reaching 8.3%. As the freeze-thaw cycles increases, the frost heaving displacement and the relative freeze-thaw displacement will gradually drop off.
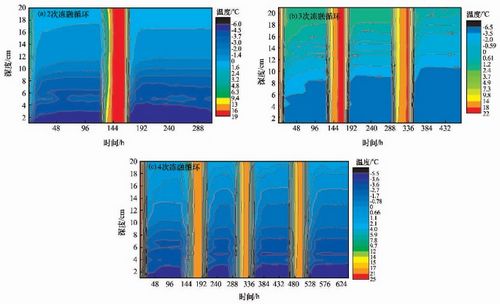
The isothermal cloud diagrams of Tibetan silty clay for 2(a),3(b) and 4(c) freeze-thaw cycles
Download from the attachment




